Static Detection of Security Vulnerabilities in Scripting Languages
本文为Stanford大学2005年发表的文章追本溯源,这个Yichen Xie和Alex Aiken团队似乎是PHP安全静态分析比较早的,那个时候,台大的Huang等的WebSSARI应该出来了; Livshits等的Pixy也在构建中。 这一篇理论性的东西比较多,都是在构建数学模型,有借鉴意义。 再拿来总结一下。
本文提出的是一个PHP安全漏洞的静态分析算法, 他们提出了一种三层架构从块内,过程内, 过程间三个级别进行静态分析。 尝试解决脚本语言独有的一些的动态特性,如动态类型, 代码包含。
贡献
提出了一个对于PHP的过程间静态分析算法。 尝试解决一些动态语言特有的挑战, 如: 动态代码加载, 动态变量类型转化, pervasive use of hash tables and regular expression matching.
如上所说, 本文的核心方法时提出了一种三层结构, 利用隔离处理,想上传播的思想。 在
intrablock,intraprocedural, andinterprocedual三个level上做文章。 如在每个BB(basic block)中, 作者尝试利用符号执行去model动态特征(dynamic features), 然后将结果生成block summaries, 这些summaries供上层分析使用, 从而帮助我们hidden了下层内部的复杂结构。本文使用上述静态分析方法寻找SQL注入, 但是we believe that, with small modifications, the same techniques can be applied to detecting other vulnerabilities such as XSS and code injection in web applications.
本文experimentally validate our approach by implementing the analysisi algorithm and running it on 6 popular web application written in PHP. 找到了105个0day.
Scripting Language Dynamic Feautres
每次遇到这个章节, 我都想总结一下:
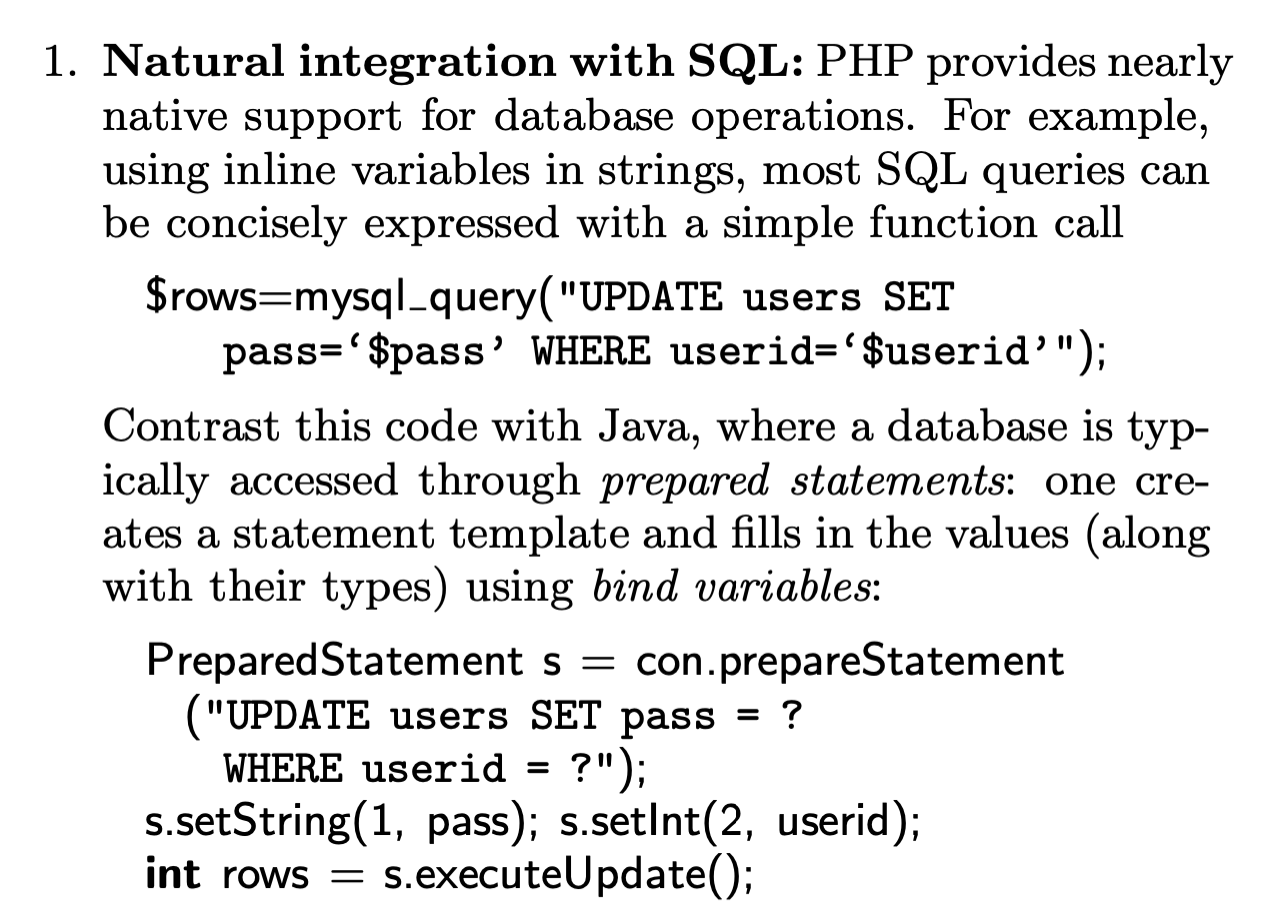
如上例子, 作者对比了PHP与JAVA构造SQL语句时的不同,JAVA用的是prepared statements(当然PHP引入PDO后也是这样,但是int类型还是会出问题)。而PHP直接拼接字符串(natural integration)。

implicit casting 主要涉及到字符串,这种web app中最常见的输入。 在代码中常常做出各种诡异的转化。


如使用,extract会根据参数讲数组的键值映射成变量,(这一块没太看清楚,可能就是讲extract这种函数动态向符号表引入变量)。
ANALYSIS
本文主要的贡献是还是一些理论上的形式化分析, 没有看到工程上的东西。
步骤:
- 生成AST
AST: 将PHP解析成抽象语法树(用的PHP5.0.5), 还是以文件为单位的, 将文件中无封装的无的语句作为main function, 每一个文件有一个main, 0-N个user-defined function, 分析从main function开始。
- 建BB,建CFG
分析文件中的每个function的ast。 划分BB,本文用的粒度是single entry, single exit sequences of tatements(看到还有以单条statement为粒度的)。然后构建CFG,遇到conditional jumps在CFG edge上label branch predicate。
Simulated using Symbol execution
对每一个基本块, 作者使用了动态特性去理解块中的每一条statement对global state of the program所带来的影响,并将这些信息记录成summary。
Reachability analysis
即数据流的可达性分析, 建立在构造好summaries的块之上,combine
block summariesinto afunction summary, 此时function summary建立了(即第二层),每个function summary描述了pre- and post-conditions of a function处理calls
在function内做可达性分析时, 难免会遇到其他过程的调用,此时需cover。
具体来看:
1. Simulate Basic
在语言建模的基础上,完成转化,生成每个块的summary(BlockSummary)
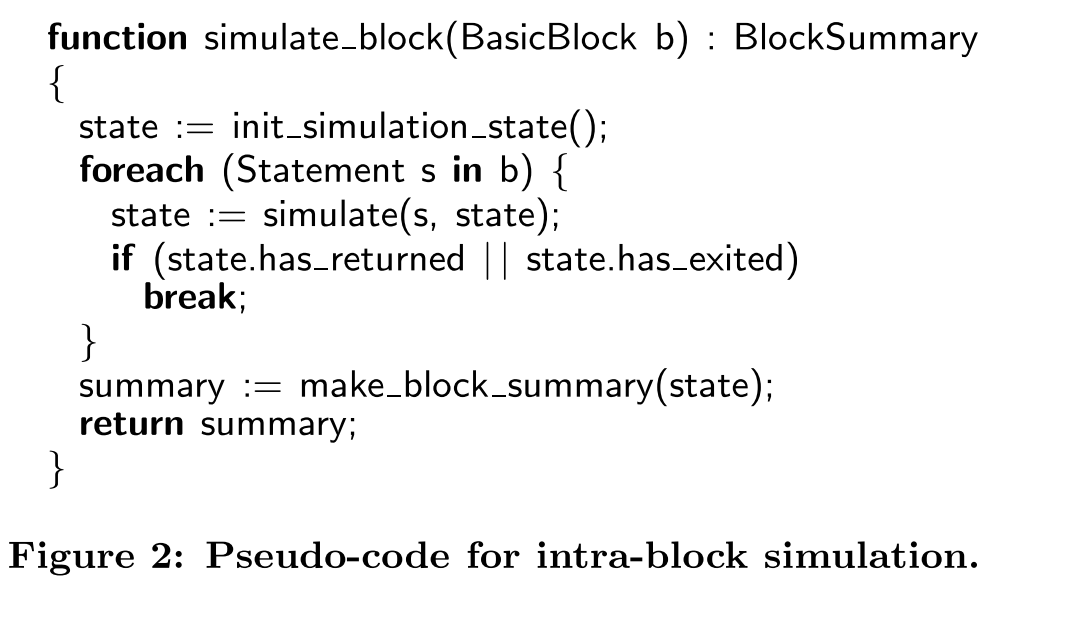
这个总的算法,输入为一个基本块,初始一个state 用来初始化块中变量状态(x->x0) 。 并在循环中迭代更新状态,如果遇到return和exit,则为出口;end block(迭代完成)也为出口,过程间分析时遇到exit也为出口。用每一个基本块的simulate后的state做一个summary, 然后返回这个块的summary。
intra-block simulation的关键 问题就是在于如何simulate state, 以下讨论simulation process:
## Language: 先对语言进行建模

在此作者根据需求, 对PHP语言进行建模, 形成了一个子集:
变量值类型(Value Type): 字符,布尔,数组,静态无法确认的数据(如形参)
常量值类型(Constant): 字符串,数字,true, false, null
L-val(location value),这里有variable x, 实参,array
表达式(Expression):常量表达式,变量表达式, 二元操作表达式, 一元操作表达式, 表达式类型转化。
语句(Statement): 赋值语句(表达式运算),赋值语句(过程调用) ,返回值语句return, 退出语句exit,包含语句include。
其中提到了,include这种statement是scripting language所特有的(which allows prorammers to dynamically insert code into the program)。
Simulation State(Memory Location -> Value)
Simulation State 是一个映射, 此映射: Memory Location->their value representations, 此处的memory location 指的是一个program variable(e.g., x), 或者a hash table accessed via another location(e.g. x[key]).

The simulation state maps memory locations to their value representations
图(a)是完整的表述。这一段就是形成一个Location到value的映射。
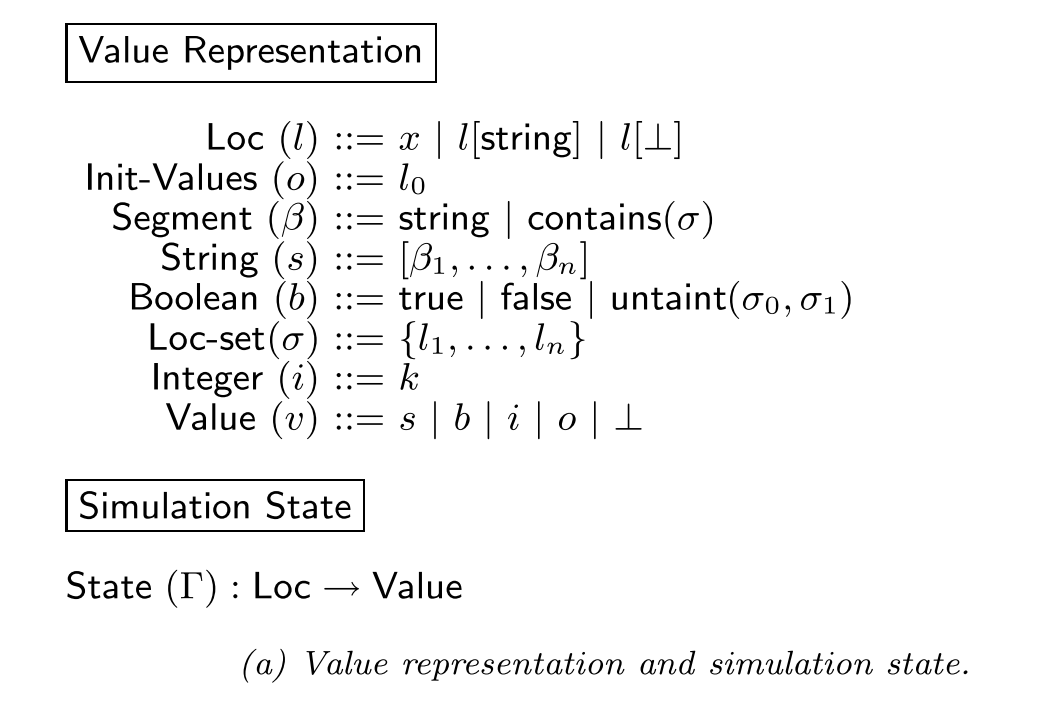
在开始分析的时候, Loc会被初始化为一个L0, 组成了simulation的初始状态集合。然后迭代value, 这里的value分为三类,具体看图(a)中的value representation部分,可以表示为三类分别是(String, Boolean和Integer)。
String:
String是最基本的类型,也是我们关注的类型。modeling string 的精确程度,直接影响了分析的精确性。
作者认为,
modeling concatenation well enables an analysis to better understand information flow in a script. 举例子来说,就像用户输入的GET, POST会拿来拼接SQL语句,SQL查询结果又会拼接到HTML中, 这是常见的动态web操作。因此,作者将string values are represented as an ordered concatenation of string segments,.
Boolean:
Integer:
Support track integer constants and binary and unary operations between them. We also support type cast from integers to Boolean and string values.
Locations和L-val转化规则
这里在解释L-val, 首先看模型:
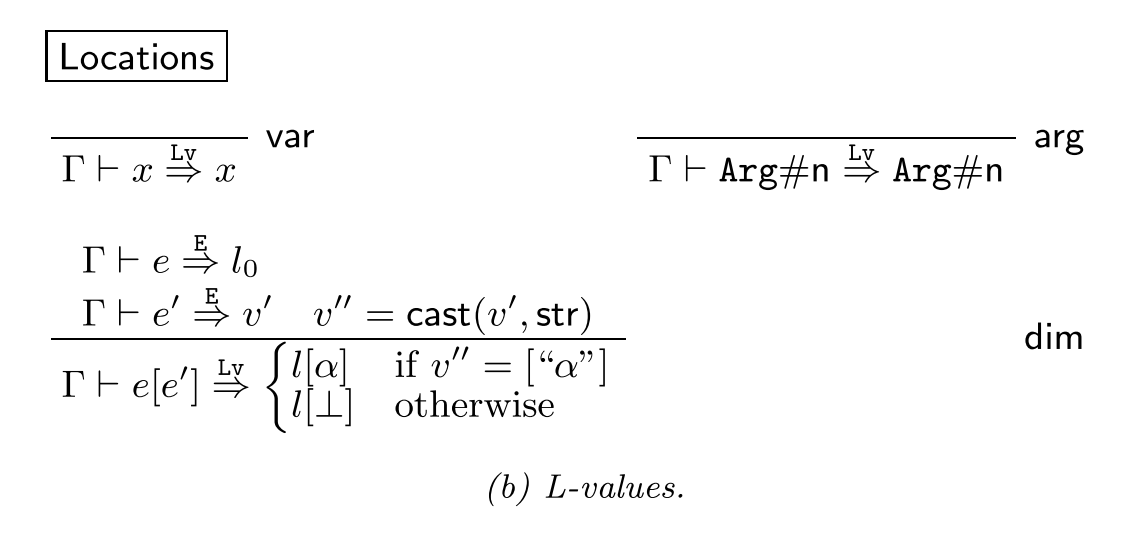
如上面对Lv的规则的定义, var, arg,dim三种(注意当时的文章都不考虑OO)。
看下边这个例子:
1 | $hash = $_POST; //$_POST这个hash table赋给$hash |
分析这段代码, 首先看初始状态
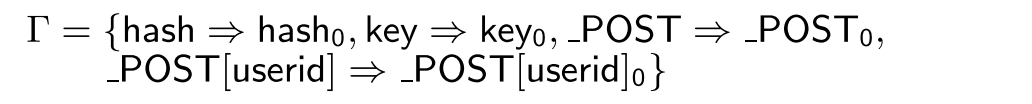
我们让每一个符号指向一个初始状态。然后根据上边的规则定义, 根据var的规则处理前两条:

他们都指向了一个unique location。
第三条来用dim的规则定义处理。此时根据横线上方两条条件规则(e是名e'是键),分别映射到_POST0和['userid']那么他将映射到L[阿尔法]中, 即_POST[userid]0。
Exp转化规则
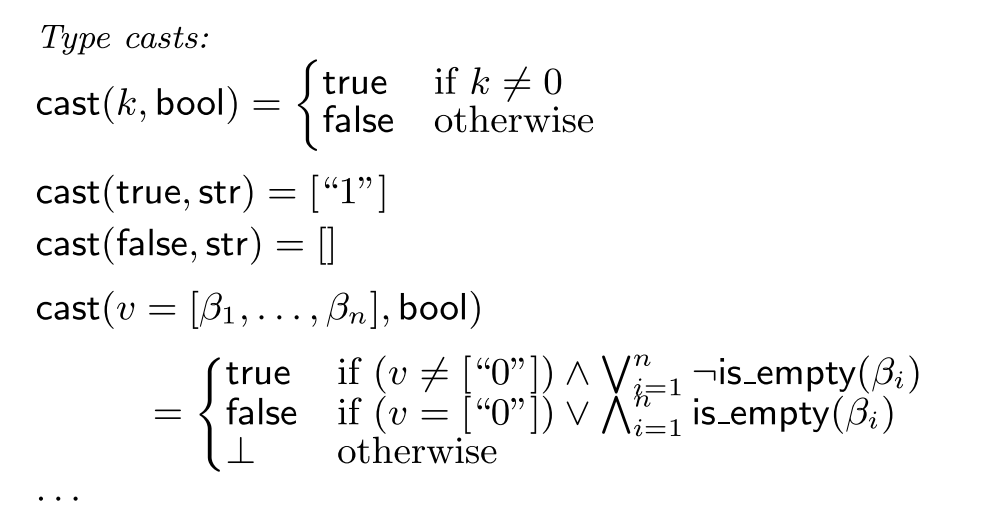
因为脚本语言是一种动态类型, 在运行解释器会选择当前运算最适合的规则(弱类型)。那么就带了了类型转化问题。

Statements转化规则
赋值有两种: 表达式计算赋值,和过程间调用赋值。 先看表达式计算如何被model:
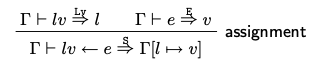
Assignment rule:
- resolves the left-hand side into a memory location l. (上式lv=>l)
- evaluates the right-hand side into a value v.(上式e=>v)
然后根据rule update the simulation state after the assignment maps l to the new value v。
Block summary
经过以上的转化后, 将块内信息转化为block summary,一个块summary是由六元组组成:
Error set: 在进入BB时,每一个variables必须是sanitized的状态。
Definitions: the set of memory locations defined in the current block.
Value flow: the set of pairs of locations (l1, l2), l1 on the entry becomes a substring of l2 on exit.
Termination predicate: 块中是否含有程序终结, true if the current block contains a exit statement, or if it calls a function that causes the progmra to terminate.
Return value: 返回值, records the representation for the return value if any, undefined otherwise.
Untaint set: 向每个后继块传递当前的未过滤变量集合(由于有分支的存在,故每一个后继得到的summary可能不同)
Intraprocedural Analysis

一个过程内的抽象,是基于他的块抽象的:
- Error set: the set of
memory locations(variables, parameters, and hash access), 因为查的是SQL注入, 所以当其中一个memory locations的value流入database query时, 必须有记录他被sanitized了,否则error - Return set: the set of parameters or global variables 进入了return value(only string)
- Sanitized values: the set of parameters or global variables,使用前向数据流可达性分析来探测被过滤输入流入每一个包含return的块。
- Program Exit: 一个指明当前function是否退出程序, 穷举所有CFG可达块。 如果没有return, 此程序就是一个exit function(也不一定,有的分支执行到最后就默认返回null了)
Interprocedural Analysis
本文的分层次污点分析的最高层, interprocedural层。分析intra的summary, 对于每一个function call点, f(e1...en)分析一下四个方面:
Pre-conditions: 使用error set 证明the set of parameters and global variables在进入该过程时都是安全的
Exit condition: 如果进入了一个exit function, 就将之后所有的stmt删除。
Post-conditions:
Return value:
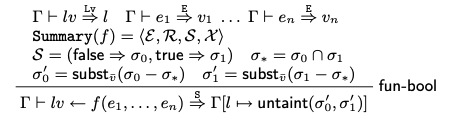

ExPERIMENTAL RESULTS

没有 False Positive, 确定没有误报?
CASE STUDY

但是我并没有看到具体的符号执行啊。
